Following a comprehensive oral examination and review of all the diagnostic material obtained for your child, our experienced clinicians will be able to discuss various treatment options for your child and the best individualised treatment approach to complete the treatment in order to restore your child’s teeth and rehabilitate the mouth to optimal health.
Fissure sealants
Tooth decay and cavities often occur on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. The good news is that fissure sealants can offer significant protection against cavities.
What causes tooth decay?
Your teeth are covered with a sticky film of bacteria called plaque. Plaque bacteria use sugar and starch in food as a source of energy. The bacteria convert the sugar and starch into harmful acids that attack the tooth enamel. Repeated attacks may cause the enamel to break down resulting in cavities.
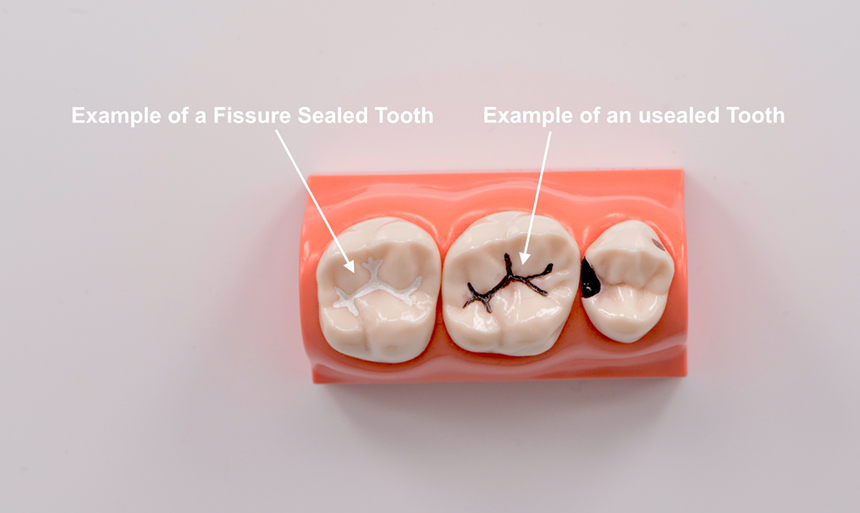
What are sealants?
Fissure sealants protect the grooved and pitted surfaces of the back teeth. These chewing surfaces of the back teeth can be difficult to clean and food can get stuck in them, which can lead to decay. The sealant, a BPA free plastic resin, bonds into the pits and fissures which acts as a barrier, protecting enamel from plaque and acids and making it easier to clean.
How are sealants applied?
The application of a sealant usually takes a few minutes to seal each tooth. The diagnosed teeth are first cleaned and dried using cotton rolls. We condition the chewing surfaces to help the sealant adhere to the tooth and then dry them. Next, we apply the sealant onto the tooth enamel, where it bonds directly to the tooth and hardens. Finally, the utilisation of a curing light helps the sealant harden. Your child will be able to eat and drink immediately after the treatment.
How long do sealants last?
As long as the sealant remains intact, the tooth surfaces remain protected from decay. Sealants usually last several years before reapplication is necessary. Sometimes however, sealants sometimes come off or wear down. During your regular dental visits, your dental professional will check the condition of the sealants and reapply them if necessary.
Are there different types of sealants?
We offer two different types/strengths of fissure sealants. We recommend the stronger type especially in children who are more prone to cavities, have enamel hypomineralisation i.e. ‘weak/ chalky’ enamel or those who grind their teeth.
Are sealants just for kids?
In children, the likelihood of developing pit and fissure decay as soon as the back teeth erupt into the mouth is much higher, hence they are obvious candidates. Adults can also be at risk for this type of decay and can also benefit from sealants as well. Ask your dental professional for more information. Prevention is the key!
Which teeth should be sealed?
The teeth most at risk of decay are the six and twelve year old molars. Many times the permanent premolars and primary or ‘baby’ molars will also benefit from sealants. In fact, any tooth with grooves and pits can benefit from sealants!
Although sealants are an excellent preventive treatment, they do not guarantee that decay will not form. Brushing and flossing regularly is still very important.
In preschool aged children, fissure sealants can also protect teeth that have lost enamel due to grinding (attrition) or acid exposure (erosion).